|
|
An
equation form used to analyze the thermal performance
capability of a specified cooling tower was required.
Currently, the following equation is widely accepted
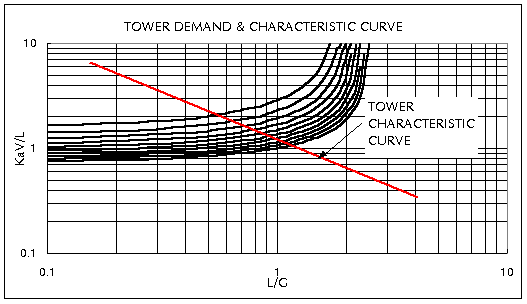
and is a very useful to be able to superimpose
on each demand curve, since KaV/L vs. L/G relationship
is a linear function on log-log demand curve.
KaV/L = C (L/G)-m
where,
KaV/L=Tower Characteristic,
as determined by Merkel equation
C=Constant related to the cooling tower design,
or the intercept of the characteristic curve at
L/G=1.0
m=Exponent related to the cooling tower design
(called slope), determined from the test data
The characteristic
curve may be determined in one of the following
three ways;
|
|
(1)
If still applicable and available, the vendor
supplied characteristic curve may be used.
In all cases the slope of this curve can
be taken as the slope of the operating curve.
(2) Determine by field testing one characteristic
point and draw the characteristic curve
through this point parallel to the original
characteristic curve, or a line through
this point with the proper slope (- 0.5
to - 0.8).
(3) Determine by field testing at least
two characteristic points at different L/G
ratios. The line through these two points
is the characteristic curve. The slope of
this line should fall within the expected
range, and serves as a check on the accuracy
of the measurement.
|
A characteristic point
is experimentally determined by first measuring
the wet bulb temperature, air discharge temperature,
and cooling water inlet and outlet temperature.
The L/G ratio is then calculated as follows;
|
|
(1)
It may be safely assumed that the air discharge
is saturated. Therefore, the air discharge
is at its wet bulb. Knowing wet bulb temperature
at the inlet of tower, the enthalpy increase
of the air stream can be obtained from a
psychrometric chart. Air and water flow
rates have to be in the proper range for
uniform flow distribution. In case of recirculation
of the air discharge, the inlet wet bulb
may be 1 or 2oF above the atmospheric
wet bulb temperature.
(2) From a heat and mass balance the dry
air rate and the prevailing L/G ratio in
the tower can be calculated [L/G = D ha
/ (Cw x (tw2 - tw1))]
|
Next, the corresponding
KaV/L value has to be established. This is simply
done by plotting the calculated L/G and approach
on the demand curve for the proper wet bulb and
range.
|