|
1) Torque
This is very important factor
to know the required torque of fan and to decide the
load acceleration of motor.
5252
x Brake Horse Power of Fan
Torque = ---------------------------------------------------
(lb-ft)
RPM of Fan
Where, 5252 = Unit Conversion
Correction Coefficient
[Horse Power = Force x Distance / Time
= Force x Velocity (velocity = distance / time = radius
x angular speed)
= Force x Radius x Angular Speed (angular speed = 2
p x rpm / 60)
= Force x Radius x 2 p x
RPM / 60
= Torque x 2p x RPM / 60
(torque = force x radius)]
60 x Horse
Power 60 x 76 Kg M/Sec (HP)
Acc'ly, Torque = ----------------------------- = ----------------------------------
2 p x RPM
2p x RPM
60 x 76 x 2.2046 x 3.281 HP
(1 Kg = 2.2046 lb)
= ----------------------------------------- (1
m = 3.281 ft)
2p x RPM
5252 x HP
= ---------------- (lb-ft)
RPM
- ● The relationships between
the speed of fan and BHP of fan are as follows;
HPrequired at 1/4 of fan full speed
= (1/4)3 HPdesign at fan full speed
HPrequired at 2/4 of fan full speed = (2/4)3
HPdesign at fan full speed
HPrequired at 3/4 of fan full speed = (3/4)3
HPdesign at fan full speed
- ● The relationships between
the speed of fan and torque of fan are as follows;
5252 x (1/4)2 HPdesign at fan full speed
Torque at 1/4 of fan full speed = ----------------------------------------------------------------
RPM of fan x 0.95 of
System Efficiency
5252 x (2/4)2 HPdesign at fan full speed
Torque at 2/4 of fan full speed = ----------------------------------------------------------------
RPM of fan x 0.95 of
System Efficiency
5252 x (3/4)2 HPdesign at fan full speed
Torque at 3/4 of fan full speed = ----------------------------------------------------------------
RPM of fan x 0.95 of System
Efficiency
- ● Meantime, the speed-torque
at the side of motor shaft load shall be converted
as follows;
5252 x (1/4)2 HPdesign at fan full speed
Torque at 1/4 of motor full speed = --------------------------------------------------------------------------------
RPM
of motor x 0.95 of Sys. Effi. x 0.95 of Gear Effic.
5252 x (2/4)2 HPdesign at fan full speed
Torque at 2/4 of motor full speed = ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
RPM of motor x 0.95 of Sys. Effi. x 0.95 of Gear Effic.
5252 x (3/4)2 HPdesign at fan full speed
Torque at 3/4 of motor full speed = ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
RPM of motor x 0.95 of Sys. Effi. x 0.95 of Gear Effic.
2) Radial Force
The only normal radial force
would be due to the minimum and maximum balance tolerance
on the blades, usually 5-8 in-lbs. That is, if one blade
have a maximum tolerance and the opposite blade have
a minimum tolerance, there would be a small net unbalanced
moment about the fan centerline.
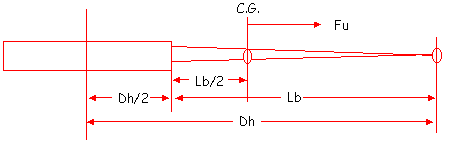
Assume we have a 5 in-lb
delta between moments : Mu = 5 in-lb. Mu is defined
as unbalanced moment. Assume we have a 14H fan with
a 22" diameter hub operating at 273 rpm (12000
tip speed).
- ● D/2 = 7.0 ft = 84 in
- ● Dh/2 = 11.0 in
- ● Centrifugal force in a
blade is concentrated at it's C.G. which is located
at approximately Lb/2
Lb = D/2 - Dh/2 = 84 - 11 = 73 in
Lb/2 = 73/2 = 36.5 in
- ● Since Mu = 5 in-lb, find
Fu (unbalanced force). Fu due to the unbalance would
be:
Mu
Fu = --------------------
Lb/2 +
Dh/2
5 in-lb
= ------------------- = 0.0105 lb
(36.5 + 11) in
- ● Centrifugal force is calculated
as:
WRN2
Fu = ----------
2934
Where,
W is lbs
R is ft to C.G.
N is rpm of fan
Fu is Centrifugal Force in lbs
In our example,
W = 0.105 lb
R = [ (Dh / 2) + (Lb / 2) ] = 11 + (73 / 2) = 47.5 in
= 3.96 ft
N = 273 rpm
Find Fu
0.105
lb x 3.96 ft x 2732
Fu = ------------------------------------ = 10.56 lbs
2934
This would be the unbalanced
centrifugal force acting horizontally at the center
of the fan hub for the example fan. To calculate the
above for a specific fan, the hub diameter, balance
moment tolerance and rpm must be known. Generally these
forces are very small due to a small allowable variation
of balance tolerance. Radial unbalance force will never
be a real concern for typical gears used in cooling
towers. However, the bearings of gear reducers are sometimes
required to check if they are properly selected with
the radial force data indicated on the catalog of gear
reducer. Even the maximum load if you lose a blade will
injure a gearbox.
3)Axial Thrust Load (Live
Load)
This load is an axial force
opposite to the airflow direction due to the operation
of fan. When you design the support beam for mechanical
equipment and you want to check if the bearings of gear
reducers selected is suitable, it is quite necessary
to evaluate the axial thrust load. This load is calculate
by:
Axial Thrust Load = Const.
x Actual Total Press. x Net Fan Area (lb)
Where,
Const. = Unit Conversion Correction Factor, 5.202 (1"
Aq = 5.202 lb/ft2)
Act. Total Press. = V.P. + S.P. (inch Aq.)
Net Fan Area (NFA) = (p /
4) x [ (Dia. of fan)2 - (dia. of seal disc)2
] (ft2)
The diameter of seal disc.,
which prevents a negative airflow at the center of fan,
is generally 0.2 to 0.25 times to the diameter of fan.
For example, in case of fan diameter = 28 ft, actual
total pressure = 0.6787" Aq., axial thrust load
= 5.202 x 0.6787 x (p / 4)
x (282 - 7.33332) = 2,024.85 lb.
But in induced draft cooling tower the fan weight must
be added to axial thrust load above. Of course, there
is no need to add the fan weight in forced draft cooling
tower (horizontal shaft).
|


